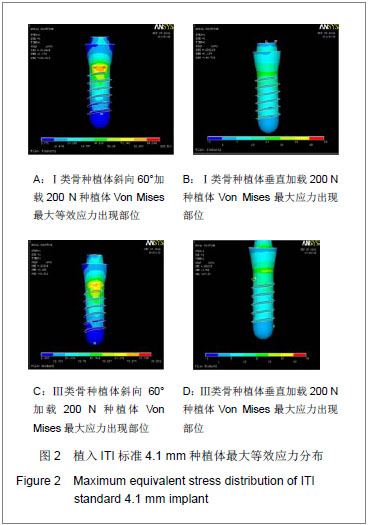
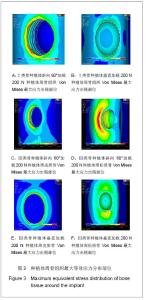
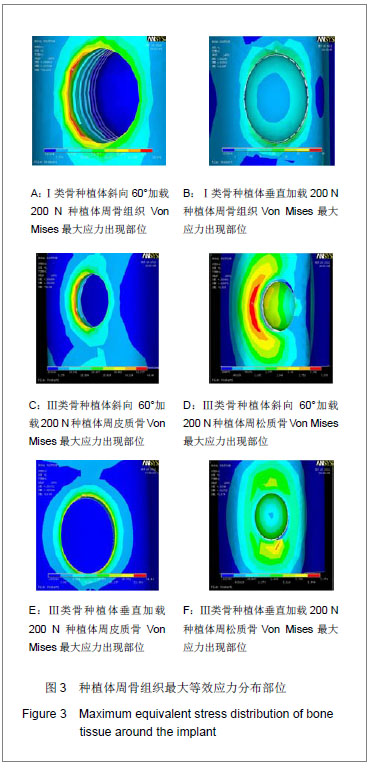
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (28): 5164-5170.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.28.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Three-dimensional finite element analysis of buccal-lingual mandibular width
Zhang Jia-yu, Cui Jie, Liu Qin, He Hui-yu
- The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2013-07-09Published:2013-07-09 -
Contact:He Hui-yu, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China hehuiyu01@126.com -
About author:Zhang Jia-yu, Studying for master’s degree, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China zjyxjykdx@163.com -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81060088*;
Science and Technology Supporting Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 201291173*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jia-yu, Cui Jie, Liu Qin, He Hui-yu. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of buccal-lingual mandibular width[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(28): 5164-5170.
share this article

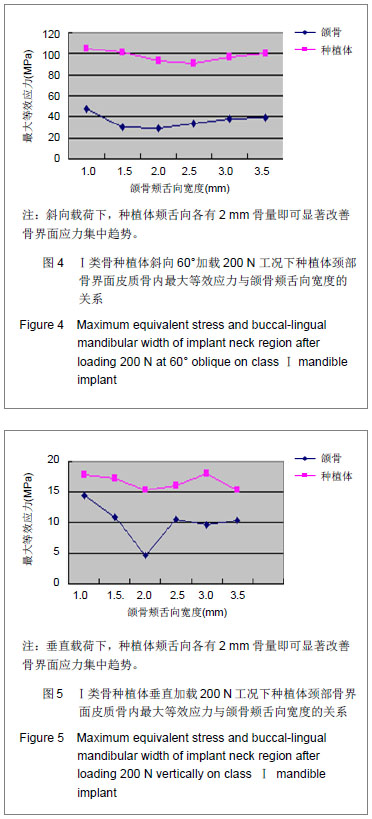
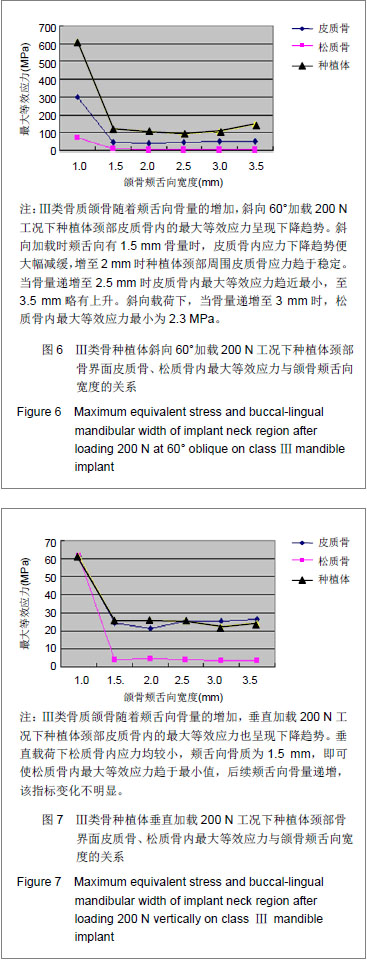
在计算机工作站运用ANSYS12.0软件对各实验组施加静载荷,分析种植体-骨界面皮质骨、松质骨内最大米塞斯应力值。研究所示当种植体周颊舌向骨量按一定程度增加时,种植体-骨界面皮质骨、松质骨内应力逐渐降低。且相同工作状况,同一模型在斜向载荷下产生的最大等效应力明显大于垂直载荷下的等效应力。 由图4,5所示可见:Ⅰ类颌骨骨质类型随着种植体周颊舌向骨量的增加,斜向60°及垂直加载200 N工况下种植体颈部骨内的最大等效应力均呈下降趋势。垂直及斜向载荷下,种植体颊舌向各有2 mm骨量即可显著改善骨界面应力集中趋势,斜向载荷下颊舌向骨量继续累加至2.5,3,3.5 mm时骨界面应力变化不大,垂直载荷下,当颊舌向骨量从2 mm加至2.5 mm时种植体周最大等效应力呈现短暂反弹上升,后续颊舌向骨量增加未见种植体周呈现明显应力变化。说明在垂直和斜向载荷下,种植体颊舌向各有2 mm骨量即可显著改善骨界面应力集中趋势。 由图6,7可见:Ⅲ类骨质颌骨随着颊舌向骨量的增加,斜向60°及垂直加载200 N工况下种植体颈部皮质骨内的最大等效应力也均呈现下降趋势。斜向加载时颊舌向有1.5 mm骨量时,皮质骨内应力下降趋势便大幅减缓,增至2 mm时种植体颈部周围皮质骨应力趋于稳定。当骨量递增至2.5 mm时皮质骨内最大等效应力趋近最小,至3.5 mm略有上升。斜向载荷下,当骨量递增至 3 mm时,松质骨内最大等效应力最小为2.3 MPa;垂直载荷下松质骨内应力均较小,颊舌向骨质为1.5 mm,即可使松质骨内最大等效应力趋于最小值,后续颊舌向骨量递增,该指标变化不明显。"
| [1]Sones AD.Complications with osseointegrated implants.J Prosthet Dent. 1989;62(5):581-585.[2]Kirsch A, Ackermann KL.The IMZ osteointegrated implant system.Dent Clin North Am. 1989;33(4):733-791.[3]de Almeida EO, Rocha EP, Freitas AC Jr,et al.Finite element stress analysis of edentulous mandibles with different bone types supporting multiple-implant superstructures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010;25(6):1108-1114.[4]陈霞云,陈松龄,张美超.下颌后牙区不同骨质内种植体即刻负载的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2011,46(4):233-236.[5]韩科.种植义齿[M]. 北京:人民军医出版社,2007.[6]宿玉成.现代口腔种植学[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2004: 187-215.[7]Lekholm U, Zarb GA. Patient selection and preparation. Braemark PI, Zarb GA,Albrektsson T.Tissue-Integraed prostheses:osseoninte-gration in clinical dentistry. Chicago: Quintessence, 1985:199-209.[8]陈良建,何浩,李益民,等.不同结构的牙种植体骨界面应力的有限元分析[J].中国有色金属学报:英文版,2011,21(7): 1602-1610.[9]马攀,刘洪臣,李德华,等.三种螺距对种植体初期稳定性影响的有限元研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2007,8(1):47-50.[10]袁佳,吴新中,李春生,等.植骨对种植体骨界面应力影响的有限元分析[J].中华全科医学,2010,8(4):417-419.[11]Lin CL, Chang SH, Wang JC.Finite element analysis of biomechanical interactions of a tooth-implant splinting system for various bone qualities.Chang Gung Med J. 2006;29(2): 143-153.[12]Sevimay M, Turhan F, Kiliçarslan MA,et al.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effect of different bone quality on stress distribution in an implant-supported crown.J Prosthet Dent. 2005;93(3):227-234.[13]丁熙,朱形好,廖胜辉,等.牙种植体即刻负载骨界面应力分布的三维有限元分析[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2007,12(2):60-64.[14]臧晓霞,孔亮,刘宝林,等.包含直径和长度连续变化种植体骨块三维有限元模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(1):115-117.[15]兰晶,徐欣,姜广水,等.2种接连方式种植体的骨界面应力分析[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2008,26(4):443-447.[16]林东,林珊,陈江,等.不同螺纹深度微小种植体的生物力学三维有限元研究[J].福建医科大学学报,2009,43(5):381-383.[17]胡妍,王冬梅,王成焘,等.四单位种植固定桥不同设计方案的生物力学研究[J].上海交通大学学报,2009,43(7):1056-1061.[18]Lin CL, Kuo YC, Lin TS.Effects of dental implant length and bone quality on biomechanical responses in bone around implants:A 3-D non-linear finite element analysis.Biomedical Engineering.2005;17(1):44-49. [19]游素兰,黄远亮,孙旻,等.下颌4枚与6枚种植体全口固定义齿的有限元分析[J].上海口腔医学,2009,18(6):567-571.[20]Duyck J, Rønold HJ, Van Oosterwyck H,et al.The influence of static and dynamic loading on marginal bone reactions around osseointegrated implants: an animal experimental study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001;12(3):207-218.[21]仇敏,王继玲,惠光艳,等.骨质量对种植牵张初期稳定性影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(48): 9100-9103.[22]Duyck J, Van Oosterwyck H, Vander Sloten J,et al. Magnitude and distribution of occlusal forces on oral implants supporting fixed prostheses: an in vivo study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000;11(5):465-475.[23]邬铭峰,罗涛,王亚敏,等.三维有限元法在口腔医学中的应用[J].广东牙病防治,2007,15(1):36-38.[24]朱强,汪大林,邱小倩.逆向工程法建立下颌第一磨牙种植体有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(4):637-640.[25]Motoyoshi M, Yano S, Tsuruoka T,et al.Biomechanical effect of abutment on stability of orthodontic mini-implant. A finite element analysis.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005;16(4):480-485.[26]Chun HJ, Shin HS, Han CH,et al. Influence of implant abutment type on stress distribution in bone under various loading conditions using finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006;21(2):195-202.[27]王海力,郑立,王晓洁,等.下颌骨模型精确度对种植体周围应力分布的影响[J].中国口腔种植学杂志, 2006, 11(1): 5-8.[28]沈山,张国志.加载方向对种植体骨界面上应力分布的影响[J].暨南大学学报:自然科学与医学版, 2004,25(2): 198-201.[29]都吉秀,叶平,吴润发,等.双根单冠种植修复下颌第一磨牙的三维有限元分析[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2008,13(1):1-5.[30]金鼎,杜暘,屈直,等.下颌第一磨牙不同冠根比种植修复体的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13): 2354-2357.[31]李翠,郭新程,韦艺,等.应用三维有限元法对不同骨质牙种植修复体生物力学的研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2011,21(1):15-18.[32]陈治清.最新口腔材料学[M].成都:四川科学技术出版社,1989: 463.[33]华筑信,刚芹果,林振福,等.未成年人胫骨近端松质骨的力学性质及讨论[J].中国生物医学工程学报,1998,17(4):355-357.[34]Zhao JH, Zhou YM, Li CY. Finite element analysis of the effects of implant thread locations on stress distribution.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008;26(6):584-587.[35]Maeda Y, Miura J, Taki I,et al. Biomechanical analysis on platform switching: is there any biomechanical rationale.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007;18(5):581-584.[36]郑群英,杨秋燕,杜志斌,等.前牙区平台转换种植体不同种植深度的生物力学分析[J].医用生物力学,2010,25(5):417-421.[37]孙健,熊耀阳,李元超,等.功能梯度牙种植体三维有限元力学分析与结构优化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(48): 8960-8963.[38]Watari F,Yokoyama A,Omori M,et al.Biocompatibility of materials and development to functionally graded implant for bio-medical application. Composites Science and Technology. 2004;64(6):893-908.[39]Sadollah A, Bahreininejad A.Optimum gradient material for a functionally graded dental implant using metaheuristic algorithms.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4(7):1384- 1395. |
| [1] | Zhang Guomei, Zhu Jun, Hu Yang, Jiao Hongwei. Stress of three-dimensional finite element models of E-MAX porcelain inlay [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 537-541. |
| [2] | Huo Hua, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Jian, Hong Wei. Effects of drug coating on implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [3] | Zhao Chuntao, Qing Mingsong, Yu Langbo, Peng Jiachen . Meta-analysis of total knee arthroplasty guided by kinematic alignment and mechanical alignment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1435-1442. |
| [4] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [5] | Xu Guofeng, Li Xuebin, Tang Yifan, Zhao Yin, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun. The role of autophagy in ossification of the human ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1174-1181. |
| [6] |
Cen Yanhui, Xia Meng, Jia Wei, Luo Weisheng, Lin Jiang, Chen Songlin, Chen Wei, Liu Peng, Li Mingxing, Li Jingyun, Li Manli, Ai Dingding, Jiang Yunxia.
Baicalein inhibits the biological behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma stem cells by downregulation of Decoy receptor 3 expression |
| [7] | He Yujie, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Cai Yongqiang, Dai Lina, Xu Yangyang, Wang Yidan, Xu Xuebin. Digital measurements of the anatomical parameters of pedicle-rib unit screw fixation in thoracic vertebrae of preschoolers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 869-876. |
| [8] | Yan Shu, Lu Yan, Ouyang Zhaolian. Analysis of programs on tissue engineering funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China between 2013 and 2018 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 731-735. |
| [9] | Shi Qianhui, Wu Chao, Zhou Qian, Cheng Yuting, Li Fang, Huo Hua, Qi Yuhan, Huang Xiaolin, Wang Yong, Liao Jian. Prevention and treatment of implant periapical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5434-5440. |
| [10] | Wang Hui, Zhang Yazhou, Shi Lifang. Three-dimensional model analysis of trabecular acetabular cup and solid acetabular cup [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 390-394. |
| [11] | Xue Zhipeng, Li Taixian, Li Yan, He Haijun, Huang Zeqing, Sun Jigao, Chen Weiheng. Comparison of finite element models of osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on CT gray-assigned method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 395-400. |
| [12] | Sun Jian, Fang Chao, Gao Fei, Wei Laifu, Qian Jun. Clinical efficacy and complications of short versus long segments of internal fixation for the treatment of degenerative scoliosis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 438-445. |
| [13] | Gao Yangyang, Che Xianda, Han Pengfei, Liang Bin, Li Pengcui. Accuracy of robot-assisted and fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw placement: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 446-452. |
| [14] | Zhang Jian, Wang Xiaojian, Qin Dean, Zhao Zhongtao, Liang Qingyuan, An Qijun, Song Jiefu. Risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis after spinal deformity surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 460-468. |
| [15] |
Zhang Xuan, Li Yunpeng, Zhang Xuejian, Yin Chuanrong, Deng Yue.
Guided bone regeneration using preformed titanium mesh combined with bioabsorbable membranes in aesthetic area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4112-4117. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||